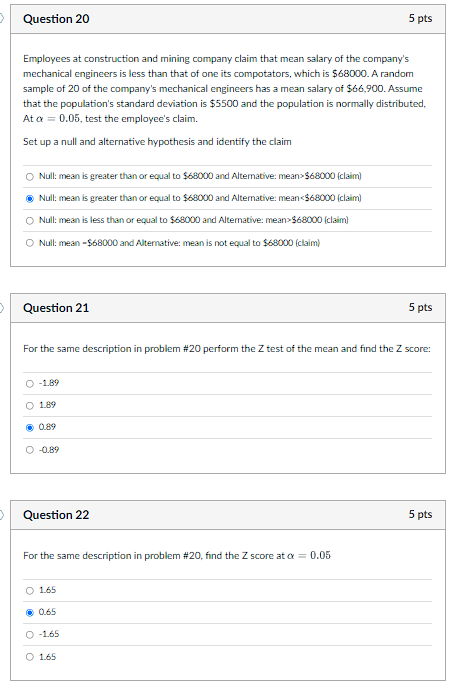
Question 20
Employees at construction and mining company claim that mean salary of the company's
mechanical engineers is less than that of one its compotators, which is $68000. A random
sample of 20 of the company's mechanical engineers has a mean salary of $66,900. Assume
that the population's standard deviation is $5500 and the population is normally distributed,
At \alpha =0.05, test the employee's claim.
Set up a null and alternative hypothesis and identify the claim
Null: mean is greater than or equal to $68000 and Altemative: mean> $68000 (claim)
Null: mean is greater than or equal to $68000 and Altemative: mean< $68000 (claim)
Null: mean is less than or equal to $68000 and Altemative: mean> $68000 (claim)
Null: mean -$68000 and Alternative: mean is not equal to $68000 (claim)
Question 21
For the same description in problem #20 perform the Z test of the mean and find the Z score:
-1.89
1.89
0.89
-0.89
Question 22
For the same description in problem #20, find the Z score at \alpha =0.05
1.65
0.65
-1.65
1.65